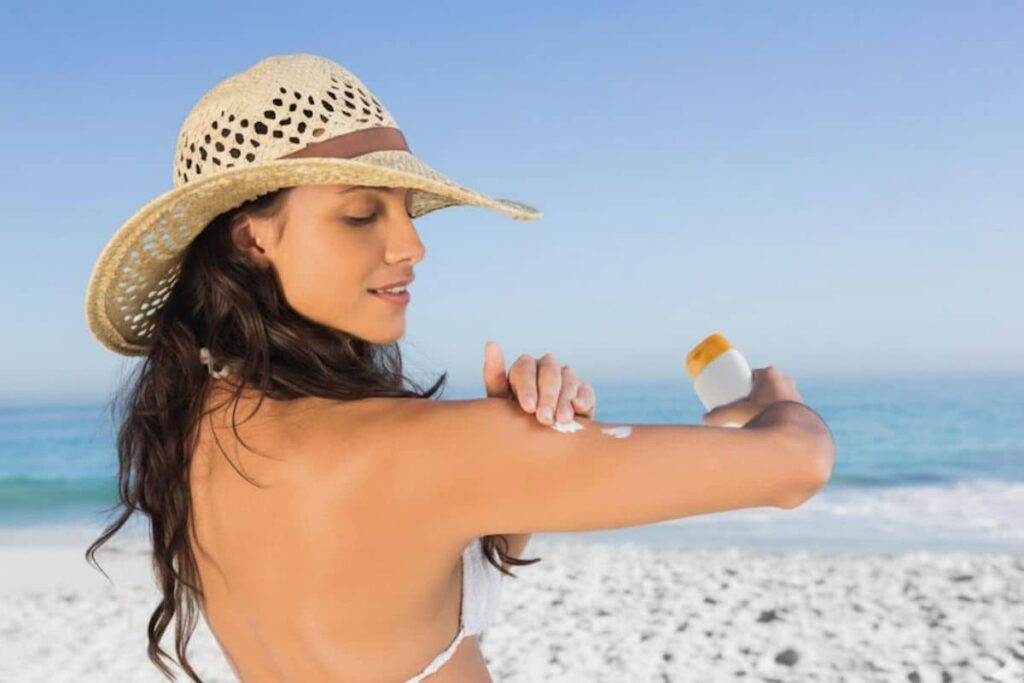
The importance of sunscreen is vital for keeping your skin healthy and protected. Daily exposure to UVA and UVB rays can cause sunburn, tanning, and premature aging. Applying sunscreen forms a protective layer, helping your skin heal, stay radiant, and maintain its youthful appearance. Regular use ensures long-term skin health while preventing pigmentation, fine lines, and sun damage.
Many people believe sunscreen is only necessary when going out in direct sunlight. The truth is, UV rays affect your skin indoors too — through windows, and even from artificial light sources like mobile phones and laptop screens. That’s why daily sunscreen use is a must. Making it a part of your morning routine ensures round-the-clock skin protection, whether you step outside or not.
Both UVA and UVB rays are harmful. UVA rays cause premature aging, while UVB rays lead to painful sunburns. Sunscreen provides broad-spectrum protection against both. With consistent use, it prevents tanning, pigmentation, and uneven skin tone, keeping your skin naturally radiant.
Sunscreen isn’t just for temporary protection; it’s a long-term investment in your skin’s health. Regular use preserves youthfulness, slows down aging, and ensures your skin remains firm and smooth over the years. People who use sunscreen consistently have fewer wrinkles, dark spots, and skin issues compared to those who don’t.
UVA rays break down collagen and elastin, the proteins that keep your skin firm and youthful. This results in fine lines and sagging skin. Applying sunscreen daily slows down this breakdown, keeping your skin tighter and more youthful for longer.
Regular sunscreen use also lowers the risk of serious concerns like skin cancer. It helps protect against pigmentation, dark patches, and redness. With proper application, your skin gradually becomes clearer, smoother, and more even-toned.
Sunscreen is important for every skin tone. Many people with dusky or wheatish skin believe they don’t need sunscreen, but UV rays damage all skin types. The difference is that fair skin shows damage more quickly, while darker tones take longer to show visible signs.
Fair skin has less melanin, which means it burns and reddens faster under the sun. Sunscreen provides the necessary protection, preventing sunburn and uneven redness.
Darker skin tones may not show immediate tanning, but UV rays still cause internal damage. Sunscreen protects deeper layers of the skin and prevents long-term issues like dark patches and dullness.
The short-term effects of sun exposure may seem like just tanning or redness, but long-term damage is far more severe. Constant UV exposure weakens the skin’s defense system, making it vulnerable to serious conditions. Sunscreen works as the first line of defense against such damage.
Studies show that people who regularly use sunscreen have a significantly lower risk of skin cancer. Sunscreen blocks harmful rays and prevents mutations in skin cells, protecting you from life-threatening conditions.
Sunburns are not just temporary redness; they damage the deeper layers of the skin, making it weaker over time. Sunscreen prevents painful burns and helps your skin remain smooth and irritation-free.
Choosing the right sunscreen is just as important as applying it. Many people buy sunscreen based only on brand or packaging, but the right product depends on your skin type and lifestyle. Always check the SPF (Sun Protection Factor) and PA rating before buying. SPF protects against UVB rays, while PA protects against UVA rays. For everyday use, dermatologists recommend at least SPF 30 with PA+++ protection.
SPF determines how long your skin stays protected from UVB rays. For example, SPF 30 means your skin is 30 times more protected from burning compared to no sunscreen. PA rating indicates UVA protection: PA+ offers minimal protection, while PA++++ offers maximum. Always pick sunscreen with high SPF and PA values.
Buying sunscreen isn’t enough; applying it correctly is equally important. If not applied properly, it won’t provide full protection. Experts suggest applying sunscreen at least 15–20 minutes before going outdoors so it can properly settle on your skin.
Most people apply too little sunscreen, which reduces its effectiveness. Dermatologists recommend the “two-finger rule” — squeezing enough sunscreen along two fingers for the face and neck. For arms, legs, and other exposed areas, increase the quantity accordingly. A generous layer ensures complete coverage.
One-time application doesn’t last all day. Sweat, dust, and wiping can reduce its effect. Reapply sunscreen every 2–3 hours when outdoors. If you are swimming or sweating heavily, even water-resistant sunscreens need reapplication.
Sunscreen should not be reserved for summers or vacations. It’s a product that must be part of your everyday skincare routine. Regular use ensures your skin is always protected, regardless of weather or location.
Many people skip sunscreen indoors, but UV rays pass through windows, and even digital devices emit blue light that harms skin. Applying sunscreen indoors is just as important as outdoors.